
Active Region – the transistor operates as an amplifier and Ic = β*Ib.Then bipolar transistors have the ability to operate within three different regions: The transistor’s ability to change between these two states enables it to have two basic functions: “switching” (digital electronics) or “amplification” (analogue electronics). Transistors are three terminal active devices made from different semiconductor materials that can act as either an insulator or a conductor by the application of a small signal voltage. The fusion of these two diodes produces a three layer, two junction, three terminal device forming the basis of a Bipolar Junction Transistor, or BJT for short.
#BIPOLAR TRANSISTOR CHARGING SERIES#
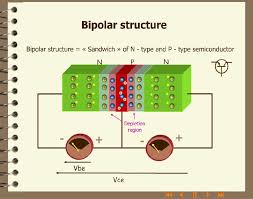
If we join together two individual signal diodes back-to-back, this will give us two PN-junctions connected together in series which would share a common Positve, (P) or Negative, (N) terminal. The bipolar transistor uses one more layer of semiconductor material to produce a device with properties and characteristics of an amplfier. These are advantages of bipolar junction transistors:īipolar junction transistors are mainly used in switching and amplification.Unlike semiconductor diodes which are made up from two pieces of semiconductor material to form one simple pn-junction. This mode is used for amplification of current. In this mode, one junction (emitter to base) is forward biased and another junction (collector to base) is reverse biased. This mode is used for switch ON application. Hence, transistor is in on mode and acts like closed switch. In this mode, both junctions are forward biased so current flows through the device. This mode is used for switch OFF application. Hence, transistor is in off mode and acts like open switch. In this mode, both junctions are reversed biased so no current flows through the device. Applying dc voltage means biasing of transistor. Transistor operates in any of these regions based on polarity of dc voltage. We need supply dc voltage to npn or pnp transistors in order to operate transistor in one of these regions. There are three modes: Cut-off mode, saturated mode, and active mode in bipolar transistor junction. The electrodes for each junction transistor are: emitter, base, and collector. In this transistor, a single n-type semiconductor layer is sandwiched between two p-type semiconductor layers.īipolar junction transistors are formed by sandwiching either n-type or p-type. In this transistor, a single p-type semiconductor layer is sandwiched between two n-type semiconductor layers. Junction transistor are also types based on their construction. Junction transistor are used more than point type transistor. There are two types of transistors, i.e., point contact and junction transistor in bipolar junction transistors. The device mode of a semiconductor is transistor. Since a semiconductor has less resistance to flow current in one direction and high resistance in another direction. Its doped between emitter and base means moderately doped, but it is always greater than emitter and base in size. Base is very lighted doped.Ĭollector − It collects charge carriers. Emitter is always greater than base.īase − Base is middle layer in BJT which is thin compared to emitter and collector. It is highly doped so that it can inject a large number of charge carriers into the base. There are three terminals in bipolar junction transistors are explained below.Įmitter − It supplies charge carriers. Terminals of Bipolar Junction Transistors
#BIPOLAR TRANSISTOR CHARGING FREE#
Electronic current is conducted by both free electrons and holes in bipolar junction transistor. The basic symbols of BJT are n-type and p-type. Unlike a normal p-n junction diode, this transistor has two p-n junctions.

It is solid state device that flows current in two terminals, i.e., collector and emitter and controlled by third device known as terminal or base terminal. A Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) is a three terminal circuit or device that amplifies flow of current.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
